Lean Agile is based on the Lean philosophy, which emphasizes the elimination of waste in all forms, including overproduction, waiting, defects, overprocessing, and unnecessary inventory. Agile, on the other hand, is a methodology that focuses on delivering software in small, incremental chunks, with a strong emphasis on collaboration and flexibility.
Read MoreStartups are going smarter day by day and they are now using new methods to save data transfer cost and improve user experience. The saving of data cost help startups to take more smart decisions while improving user experience (UX) gives additional power to SAAS/PAAS companies to grow. Read More
Hello Everybody, In previous article “Hiring Software Consultant Extra Expense Or Advantage ?” I focused on why software consultant is needed to shape your business and compared it with real world examples. In this article we are going to focus on Need of Documentation, Need of software research tools or applications or collaboration tools and how we Increase our productivity with the help of such tools. Read More
Everyone want to grow big but at what cost? The money you earn is your blood money. Without planning and investing in a good software consultant you will waste them all.
There are a countless number of IT startups come every year in market and 70% of them flush out of market because of bad management, Not having technical background or don’t know the correct path to produce business out of their product. Read More
If you are planning to scale up your IT infrastructure to cloud then this article is for you. But do managing public cloud services is as simple as managed shared hosting / dedicated hosting / VPS servers? Let’s have a look.
Key Questions to Consider Before Migrating
The public cloud has forever changed the way companies approach IT strategy. Because it can drastically reduce capital expenditures, enhance Read More
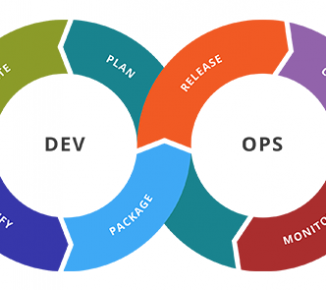
What is DevOps Anyway?
Traditionally the words of software development, testing (also known as Quality Assurance) and the IT infrastructure needed to support such activities (often called Operations) were separate worlds. The developers would write code based on requirements they were given, testers would test the features based on the same requirements (hopefully?!) and the IT staff would provide the computers, networks, and software needed by the two other groups to perform their activities. They would also be in charge of providing different environments (development, test, staging, production) that could be used by the development and testing teams. Read More










Recent Comments